Are you trying to make an international money transfer? Then you’ll need to know what IBAN and SWIFT BIC codes are and where to find them.
IBAN vs. SWIFT codes are both internationally recognized for identifying bank accounts when a transfer is being made. The specific identifier required depends on the countries involved, as well as the recipient’s bank.
A SWIFT BIC code refers to a specific financial institution in an international transaction, whereas an IBAN number identifies an individual account and the country of business. It’s the global equivalent to a bank account and an ABA routing number in the United States.
Key Differences
| IBAN Code | SWIFT/BIC Code | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | IBAN is short for International Bank Account Number. | SWIFT is short for Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) a.k.a. BIC code (Bank Identifier Number). |
| Main Functions | Used to identify an individual account in cross-border payments. | Used to identify a specific bank during an international transfer. |
| Examples | LU 28 001 94006447500003(Luxembourg) | UNCRITMMXXX(UniCredit Banca in Milan, Italy) |
| Costs | Bank transfer fees, commission, and exchange rates (3-5%). | Bank transfer fees, commission, and exchange rates (3-5%). |
| Use Cases | Used for transfers between banks and financial institutions. | Used by banks, service providers, clearinghouses, corporate business houses, brokers, etc. |
| Where to Find | Bank statement, bank website, online calculator. | Bank statement, bank website, online calculator. |
IBAN vs SWIFT
The main difference between IBAN and SWIFT lies within what the alphanumeric codes represent. In an international transaction, an IBAN code is used to identify an individual bank account, whereas a SWIFT code identifies the bank associated with that bank account.
Main Points
- IBAN and SWIFT BIC codes both facilitate international money transfers.
- IBAN is short for International Bank Account Number and is used to identify an individual account in cross-border payments.
- A SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) a.k.a. BIC code is used to identify a specific bank during an international transfer.
- The SWIFT network standardized the formats for the IBAN system and owns the BIC system.
- Oftentimes, both codes are required for an international transaction.
Power your entire partner payouts operations
98%
Customer Satisfaction
$60B+
Annual Transactions
4M+
Partners
4,000+
Customers
99%
Customer Retention
What is an IBAN Code?
An IBAN code is a long number that identifies an individual foreign bank account. It’s short for “International Bank Account Number” and includes various numeric identifiers, like the account number and country code.
This information helps financial institutions process international wire transfers faster, and with fewer errors. It acts as a method of double-checking that the transaction and bank details are correct.
What Does the IBAN Code Look Like?
The IBAN code has up to 32 alphanumeric characters that consist of:
- A two-digit country code
- A check digit code (used for detecting errors)
- A Basic Bank Account Number (BBAN) (bank, branch, and account number)
This method of bank identification is mostly used within the majority of European Union countries and other European countries.
Examples of an IBAN Code

In the register of countries that currently use an IBAN code, here are a few examples:
- Luxembourg: LU 28 001 94006447500003
- Cyprus: CY 17 002 00128 00000012005276002
- Kuwait: KW81CBKU0000000000001234560101
- Norway: NO 93 8601 1117947
Does it Cost Money to Use an IBAN?
IBAN codes are needed for international bank transfers and thus, if you’re using one, expect to pay bank transfer fees. The cost varies by different countries, but usually, there is a processing fee and commission charged by one or both banks.
Main Functions of an IBAN Code
When it comes to international banking, IBANs are a critical piece of information. It serves three main functions for sending and receiving cross-border payments, which are:
- Allows banks and other financial institutions to quickly note the country of origin for the bank.
- IBAN pinpoints the exact account number to which the money will be sent.
- It’s an easy way to double-check the accuracy of a bank’s details and ensure a transfer will be successful.
Where do I Find My IBAN Code?
Your IBAN number can be found on the top, right-hand side of your bank statement. If you can’t find the code on your paperwork, you can also find the number through online banking or an IBAN calculator tool.
Does the United States Use the IBAN System?
The United States does not use IBANs and bank accounts in the U.S. do not have IBANs. Instead, they use ABA routing numbers (for domestic transfers) and SWIFT codes (for international transfers).
The IBAN is a sort code mostly used in European countries, but recently it’s also been adopted in the Caribbean and parts of the Middle East. Although the United States and Canada do not use IBAN numbers, both recognize the system and process IBAN payments for international transactions.
What is a SWIFT BIC Code?
SWIFT is an acronym for the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication. It’s a messaging network that banks and other financial institutions use to securely transmit instructions and data through a standardized system of codes.
A SWIFT code is a standard format of a BIC. BIC is short for Bank Identifier Code. It identifies the country, city, bank, and branch when making an international transaction.
Other names for the SWIFT code include:
- SWIFT ID
- SWIFT number
- BIC ID
- BIC code
- ISO 9362
What Does a SWIFT Code Look Like?
While an IBAN identifies a bank’s country of origin and the precise account number, a SWIFT code breaks it down into three more specific elements. The unique code is comprised of 8-11 alphanumeric characters and includes:
- A four-letter bank code
- A two-letter country code
- A two-digit location code (letters and numbers)
- A three-digit branch code
The structure of a BIC code is defined by the international standard under ISO 9362:2014 and country code ISO 3166-1.
Examples of a SWIFT BIC Code
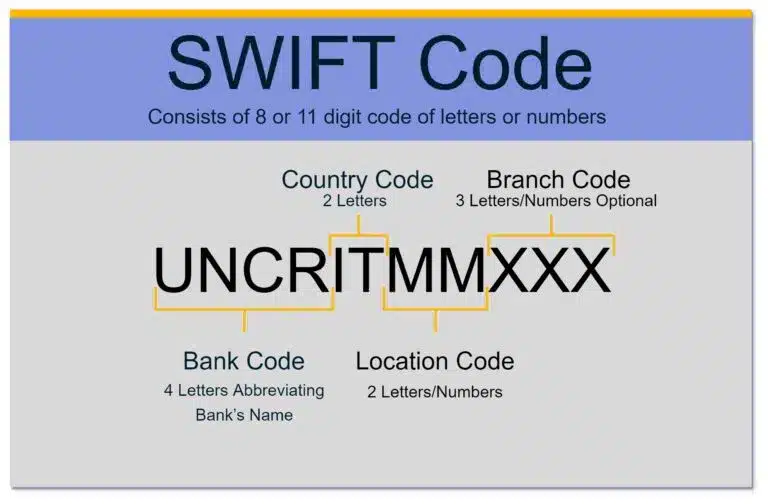
One example of a SWIFT code is for the bank UniCredit Banca in Milan, Italy, which is:
UNCRITMMXXX
- UNCR – the bank code for UniCredit Banca
- IT – the country code for Italy
- MM – the city code for Milan
- XXX – this is optional for the branch code
Does it Cost Money to Use a SWIFT Code?
When making an international transfer and using a SWIFT BIC code, expect banks to charge between 3%-5% in exchange rates.
This will vary based on the amount you send, and where it’s sent to. For larger transfers, the exchange rate will cost more than the bank transfer fees, which you should also expect.
Main Functions of the SWIFT BIC Code
SWIFT codes help banks process international wire transfers. When you use SWIFT, you’re not actually sending money, but rather, it’s a “payment order” between banks. Still, it’s the method by which the majority of global fund transfers are made.
Share Important Information
One of the main functions of the SWIFT messaging system is that it enables banks to share a significant amount of financial data. This includes critical information like:
- Account status
- Debit and credit amounts
- Details related to the transfer
Expedite Transfers
If both the sending and receiving banks have a relationship, SWIFT moves the money along immediately. The messaging system helps to expedite international payments and streamline the entire process.
How do I Find My SWIFT BIC Code?
Your SWIFT/BIC code can be located on a bank statement or through an online banking portal. If you’re not sure, you can also use a SWIFT code locator service online.
IBAN vs SWIFT BIC Code
Identification
The main difference between an IBAN and SWIFT BIC code lies in what they’re used to identify. A SWIFT code refers to a bank, while an IBAN will identify a specific bank account.
Basically, a SWIFT number tells you where to pay, and an IBAN tells you who to pay.
Messaging
While IBAN works like a bank account and routing number, SWIFT is more like a messaging system that banks use to communicate with each other. While IBAN is like a general compass, SWIFT is like the mapping coordinates. Both are important to avoid post-transaction mistakes and fees.
Coding
A SWIFT BIC code breaks down into 3 more specific elements than an IBAN code. Namely, the bank code, country code, and branch identifier. IBAN and SWIFT codes are often described as an “either/or” choice, but in reality, they are often used in conjunction.
Bank Requirements
When sending money overseas with an IBAN number, the recipient has to be in a country that supports the system. In this case, they simply give you their IBAN number.
However, in many instances, a bank requires both an IBAN number and a SWIFT code to pinpoint a recipient’s bank and specific bank account number.
If the country of the recipient does not support IBAN, SWIFT codes are the only other option. In this case, you may pick up additional fees as money will have to flow through an intermediary and/or a correspondent bank.
Use Cases
While IBAN numbers are used solely for transfers in a bank, SWIFT numbers are used by a variety of financial institutions, including:
- Clearinghouses
- Brokers/dealers
- Asset management companies
- Corporate business houses
- Service providers
…and many other types of businesses.
Why are IBAN and SWIFT Codes Important?
The mother of invention is necessity, and digital finance is no different. Prior to the global standardization of SWIFT and IBAN codes, international payments would end up in the wrong location, requiring extra fees and time to resolve the issue.
Before the adoption of IBAN, countries had different account number formats, which led to endless discrepancies in processing.
The result of the IBAN and SWIFT programs has been fewer errors in international transactions, with a faster transfer rate. Through the SWIFT program, a large amount of information can be shared between banks. Details embedded into the code include debit and credit amounts, account status, and data related to the transfer.
Despite all of these advantages, there are still issues that IBAN and SWIFT codes do not address, like foreign exchange rates.
Using IBAN and SWIFT
The information you need to know varies on whether you are sending or receiving international funds.
Sending Funds
Prior to initiating a transfer, always double-check the IBAN and/or SWIFT codes. Using an incorrect number can cause the transaction to be rejected and returned, which will cost you additional fees.
If you only have partial data, there are calculators available online to help you figure out an IBAN. Every bank will provide its SWIFT BIC code through its online banking site, but the best place to check is always with your intended recipient.
Receiving Funds
As a recipient, you must provide your IBAN number to anyone sending you money internationally. This is secure as no one can use an IBAN number to access funds in a bank account.
SWIFT BICs are readily accessible to every banking customer. Most banks provide this data on their website or upon request.
FAQ
Which countries use IBAN Codes?
As of May 2020, 77 countries are using the IBAN system.
Is a SWIFT code the same as a routing number?
Routing numbers are only used by U.S. financial institutions, while the SWIFT system is used by international organizations.
Routing numbers only respond to domestic transfers.
Is it safe to give out an IBAN number?
It is absolutely safe to give anyone your IBAN number as it only exposes data that allows someone to send money to you.
Should I use BIC or IBAN?
While an IBAN provides data about your individual account, the BIC code (SWIFT) the bank your account is held at. Countries that use the IBAN system will ask for both codes.
IBAN, SWIFT, and BIC Codes
It was the SWIFT network that eventually standardized the formats for the IBAN system. SWIFT owns and administers the BIC system and can identify a bank in seconds to secure payment.
IBAN, SWIFT, and BIC codes are all vital components to the overseas transfer of wealth. The well-being of international markets and trade relies on the international standards set forth by this technology.
Access to both types of financial identifiers ensures a quick and successful transfer, without any mistakes or mishaps. The type of codes you need will always depend on the banks being used, and the countries involved.
The best practice is to always get both codes before sending any money overseas.
For anyone who needs to make an international transfer, understanding how the IBAN and SWIFT/BIC systems operate is the first step.
Although you may not always avoid the costs associated with cross-border payments, knowledge of what to expect means you’re never surprised by exchange fees, commissions, and intermediary charges.

