This guide defines what a W9 form is and provides a linked Form W-9 from the IRS website. We describe the required information, who requests and fills out a form W9, how to prepare a complete Form W-9 and submit the form, and why W9 forms are important.
What is a W9 Form?
A W9 form is an IRS form used to provide a person’s Tax Identification Number (TIN) to their payer (or whomever is responsible for filing an information return with the IRS). The official name of the W9 form is the Request for Taxpayer Identification Number and Certification form.
W9 Form to Print
The IRS website (irs.gov) has a downloadable, fillable, and printable blank W-9 form PDF you can use for free to submit your W9 to a requester. Some requesters prefer that payees submit online digital information for W-9 form automation through their system.
Form W-9 is the same for all legal entities from individuals to C corporations, S corporations, LLC (limited liability company), partnerships, and trusts. It applies to independent contractors, small businesses, nonprofit organizations, and churches, for example.
Information Required on a W9 Form
The following information is required on a W9 form. Refer to the General Instructions following the form.
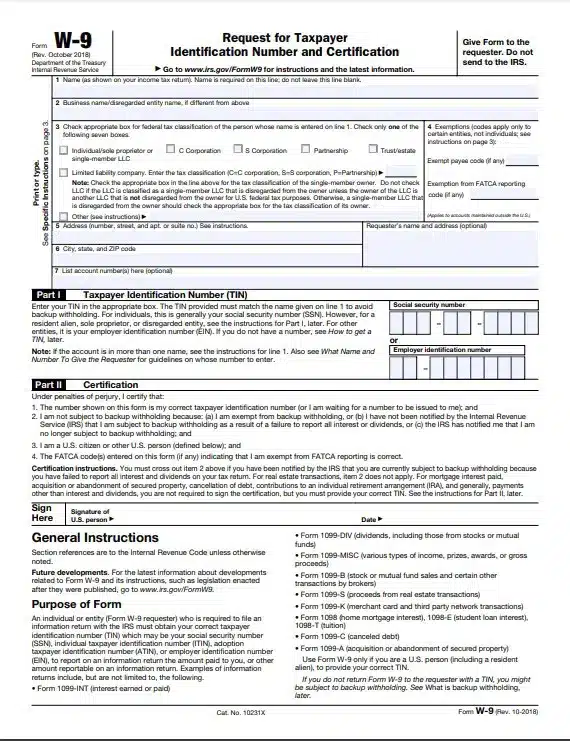
Line 1 – Name
Provide the exact name you use on your income tax return.
Individuals who have changed their last name without informing the Social Security Administration should use their first name, last name per their Social Security card, and new last name.
Per form W9 instructions, ITIN applicants should “enter your individual name as it was entered on your Form W-7 application, line 1a. This should also be the same as the name you entered on the Form 1040/1040A/1040EZ you filed with your Application.”
W9 tax form instructions for a joint account on line 1 are:
“If this Form W-9 is for a joint account (other than an account maintained by a foreign financial institution (FFI)), list first, and then circle, the name of the person or entity whose number you entered in Part I of Form W-9. If you are providing Form W-9 to an FFI to document a joint account, each holder of the account that is a U.S. person must provide a Form W-9.”
For “Other entities: Enter your name as shown on required U.S. federal tax documents on line 1. This name should match the name shown on the charter or other legal document creating the entity.”
Line 2 – Business name/disregarded entity name (if different from above)
Besides a business name or disregarded entity name, you may enter a DBA name or trade name on line 2.
Line 3 – Check one of the seven boxes for federal tax classification (type of legal entity)
The choice of seven boxes includes:
□ Individual/sole proprietor or single-member LLC
□ C Corporation
□ S Corporation
□ Partnership
□ Trust/estate
□ Limited Liability Company (LLC)
□ Other (see instructions)
For a LLC, in another box to the right of the Limited Liability Company box, enter the tax classification (C=C corporation, S=S corporation, P=Partnership).
For “Other entities: Enter your name as shown on required U.S. federal tax documents on line 1. This name should match the name shown on the charter or other legal document creating the entity.”
Line 4 – Exemptions (codes apply only to certain entities, not individuals)
Exempt payee code (if any): the instructions for Form W-9 provide 13 codes for types of exemptions from backup withholding.
Individuals (including sole proprietorship) are generally not exempt from backup withholding. Corporations are exempt from certain payments including dividends and interest, unless they fall into one of the exceptions.
Corporation exceptions requiring backup withholding include “payments made in settlement of payment card or third party network transactions. Also, corporations are not exempt from backup withholding with respect to attorneys’ fees or gross proceeds paid to attorneys, and corporations that provide medical or health care services are not exempt with respect to payments reportable on Form 1099-MISC.”
Exemption from FATCA reporting code (if any)
FATCA reporting applies to accounts maintained outside the U.S. at foreign financial institutions (FFIs). FATCA is the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act.
If applicable, insert your FATCA code A through M from the W9 form instructions or indicate “Not Applicable.” You can ask the FFI requesting form W9 whether a code is required.
Line 5 – Address (number, street, and apt. or suite no.)
Enter your current address and write NEW at the top if it differs from the address you submitted on your W9 in the payer’s records. You need to use this address to receive your form 1099 information return from the W-9 requester. The payer may still send it to your old address if included in their records.
Line 6 – City, state, and ZIP code
Line 7 – List account number(s) here (optional)
Part I – Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN)
For Taxpayer Identification, select only one appropriate box from a choice of Social Security Number (SSN) or Employer Identification Number (EIN).
If you don’t have a TIN yet, apply for it and write “Applied For” in the space for the TIN. You can get an SSN from the Social Security Administration or an EIN from the IRS. Write “Applied For” if you intend to apply soon for a TIN or have already applied. You have 60 days to receive a TIN for interest, dividends, and tradeable securities transactions payments before backup withholding is deducted.
Individuals usually use Social Security Number. Individuals may use their EIN or SSN as a sole proprietor with a registered DBA name (doing business as) or single-member LLC entity name for a small business. A resident alien not having or eligible for an SSN enters their individual taxpayer identification number (ITIN) in the Social Security Number box.
For an LLC registered as a corporation or partnership, enter the EIN.
Part II – Certifications
You will certify, under penalties of perjury, the four items listed on Form W-9. If you are subject to backup withholding because the IRS let you know you didn’t report all interest or dividends on your tax return, cross out item 2.
- You submitted a correct TIN on the W9 form or are waiting to receive a TIN.
- You aren’t subject to backup withholding for the listed reasons.
- You are a U.S. citizen or other U.S. person, as defined in the instructions.
- The FATCA codes (if any) are correct to report a FATCA reporting exemption.
The face of the Form W-9 indicates when certification or a certification item isn’t required for form W9:
“For real estate transactions, item 2 does not apply. For mortgage interest paid, acquisition or abandonment of secured property, cancellation of debt, contributions to an individual retirement arrangement (IRA), and generally, payments other than interest and dividends, you are not required to sign the certification, but you must provide your correct TIN.”
The General Instructions for Form W-9 define a U.S. person:
“ Definition of a U.S. person.
For federal tax purposes, you are considered a U.S. person if you are:
• An individual who is a U.S. citizen or U.S. resident alien;
• A partnership, corporation, company, or association created or organized in the United States or under the laws of the United States;
• An estate (other than a foreign estate); or
• A domestic trust (as defined in Regulations section 301.7701-7).”
Sign Here
Insert your signature (as a U.S. person) and the date.
Who Requests a W9 Form?
The requester of a W9 form tax document is a payer who makes IRS-specified types of payments. The payer or another entity must file a form 1099 information return to report certain types of transactions to the IRS.
You can learn more about forms W9 vs 1099 and the main differences between them.
Who Fills Out a W9 Form?
U.S. citizens and “U.S. person” payees that are self-employed independent contractors, freelancers, attorneys, businesses, vendors, suppliers, nonprofit organizations, partnerships, U.S. trusts, heirs of domestic estates, and holders of accounts in U.S. and foreign financial institutions (FFI) complete W9 tax forms requested by payers and other requesters.
How to Submit a W9 Form
Submit a W9 form to the requester (that may be the payer) required to file an information return like a 1099 form to the IRS. Do not submit the completed form to the IRS. You can submit a signed Form W-9 either electronically or on paper.
When Do You Need to Update a W9 Form?
Besides updating a W9 for a change in legal name, TIN, or contact information, you need to report a change in your exempt payee status.
According to the General Instructions for Form W-9:
“You must provide updated information to any person to whom you claimed to be an exempt payee if you are no longer an exempt payee and anticipate receiving reportable payments in the future from this person. For example, you may need to provide updated information if
you are a C corporation that elects to be an S corporation, or if you no longer are tax-exempt. In addition, you must furnish a new Form W-9 if the name or TIN changes for the account; for example, if the grantor of a grantor trust dies.”
What Types of Information Returns are Prepared from Form W-9?
Form W-9 requesters prepare different types of IRS 1099 forms, including Miscellaneous Income Form 1099-MISC and 1099-NEC for Nonemployee Compensation, 1099-INT for interest earned or paid, 1099-DIV for dividend payments, Form 1099-B for stock and mutual fund sales and other broker transactions.
Other types of 1099s are used as information returns for proceeds from real estate transactions (1099-S), canceled debt (1099-C), merchant card and third party network transactions (1099-K), and acquisition or abandonment of secured property (1099-A). W9 forms are also used for Form 1098 for mortgage interest, 1098-E for student loan interest, and 1098-T for tuition.
Importance of W9 Forms
W9 forms are important because requesters use them to collect the correct Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) and other information from each required payee to prepare a 1099 form for each calendar year. The payee uses the information to prepare their income tax return for the tax year. IRS and state tax authorities also receive a copy of the 1099s to compare 1099 income and backup withholding status to reported taxpayer income tax return amounts.
When the payee provides a correct TIN and certifications on a W 9 form and reports taxable interest and dividends on their tax return, they will not be subject to backup withholding. Backup withholding of U.S. federal income taxes is a 24% deduction from their payment received. The W9 form submitter will avoid penalties by submitting a correct TIN and accurate information for backup withholding.
Per the IRS General Instructions for Form W-9, types of penalties are described:
“Failure to furnish TIN. If you fail to furnish your correct TIN to a requester, you are subject to a penalty of $50 for each such failure unless your failure is due to reasonable cause and not to willful neglect.
Civil penalty for false information with respect to withholding. If you make a false statement with no reasonable basis that results in no backup withholding, you are subject to a $500 penalty.
Criminal penalty for falsifying information. Willfully falsifying certifications or affirmations may subject you to criminal penalties including fines and/or imprisonment.
Misuse of TINs. If the requester discloses or uses TINs in violation of federal law, the requester may be subject to civil and criminal penalties.”
Filers of 1099 information return forms prepared from W9s can use the TIN Matching service available through the IRS website.
TIN Matching compares each Taxpayer Identification Number and name combination to validate. It provides more accurate information to the Internal Revenue Service. If 1099 filers don’t misuse the TINs reported and use TIN matching to avoid an incorrect TIN, they won’t receive as many backup withholding and penalty notices.
Conclusion
Understanding what an IRS W-9 Form is, how to properly fill it out, and how to avoid penalties is important when tracking and reporting payments to your company’s suppliers on a 1099. AP automation software helps you achieve these goals. To improve global tax compliance, access the white paper.

