
Simplify your cross-border payment processes with Tipalti. The most complete international payment solution loved by 5,000+ businesses.
The Cross-Border Payments Regulation promotes efficient and transparent payments across the EU.
However, since Brexit, the rules for UK businesses look different, making visibility, efficiency, and control more important than ever.
This guide explains what the Cross-Border Payments Regulation means operationally for UK finance teams — how it affects payouts, costs, FX, SEPA routing, and scalable workflows.
We’ll also share practical steps to help you streamline payment processes, reduce costs and stay compliant.
Key Takeaways
- The Cross-Border Payment Regulation (CBPR) ensures equal fees and greater transparency for euro payments in the EU.
- Since the UK left the EU, the CBPR rules look different to UK businesses, resulting in potentially higher transaction costs, slower transfers, and strategic challenges.
- Businesses can optimise cross-border EU payments with a SEPA-friendly automation solution and standardised workflows to reduce fees and improve predictability.
- Tipalti helps UK businesses manage EU and global payments from a central account, enabling them to regain efficiency, compliance, and control over mass payments post-Brexit.
What is the Cross-Border Payments Regulation?
The Cross-Border Payments Regulation (CBPR) is a European Union (EU) law that ensures cross-border payments within the EU are charged at the same rate as domestic payments.
The regulation (EC 924/2009) was first introduced by the European Parliament in 2009 (then amended in 2021 and 2024) to facilitate cross-border trade and standardise payments across EU member states.
The amended regulation has three main aims:
| CBPR Requirement | What It Means |
|---|---|
| 1) Equalise fees | Bank and payment service providers (PSPs) must match fees for cross-border euro transactions (e.g., credit transfers, card-based transactions, or ATM withdrawals) with those for domestic transactions. |
| 2) Increase transparency | PSPs must clearly disclose total currency conversion charges so customers know what they’ll pay in their national currency before making a payment. |
| 3) Improve SEPA efficiency | CBPR supports the Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA) framework, making cross-border payments as fast and cost-effective as national payments. |
Here’s an example of how the CBPR affects cross-border business:
Before the Cross-Border Payments Regulation, a UK business paying a freelancer in France €1,000 might have to pay £20 in international transfer fees, plus foreign exchange (FX) markups.
With the regulation in force, banks in the EU have to charge the same fee for a cross-border payment as for an internal market payment.
So, the same €1,000 transfer might cost a few pence, significantly reducing costs and making cross-border commerce more appealing.
The regulation ensures equality for customers and suppliers, making it easier for businesses to expand market reach and serve a global customer base.
However, with Great Britain no longer part of the EU, the rules around cross-border payments for UK businesses have shifted. Let’s take a look at what this means for your company.
What the Cross-Border Payments Regulation Means for UK Businesses
Post-Brexit, Regulation (EU) 2019/518 no longer directly applies to UK-based businesses, so cross-border payments look different.
From the EU’s perspective, the UK is a “third country.” This status is the same as that of other countries or territories that aren’t members of the European Union or the European Economic Area (EEA).
“Third country” status means banks don’t have to charge the same fees for euro payments to the UK as they do within the EU. Many European banks now treat UK transfers as international payments, which increases fees and processing time.
The same goes for payments from the UK to the EU. Equal fees rules don’t apply, so UK businesses sending cross-border payments face higher bank charges and FX spreads.
Let’s return to our example of paying a freelancer in France €1,000.
Before Brexit, your UK bank had to charge the same fee on your €1,000 payment as they would if you were paying £1,000 to a UK company.
Now, your bank can charge a foreign payment fee, and your freelancer’s bank in France can do the same. Plus, you might have an FX conversion markup, further shrinking your margins.
However, the CBPR isn’t fully obsolete in the UK. EU rules around transparency have been “onshored” into UK law following the end of the Brexit transition.
Under the amended law and the UK’s Payment Services Regulations (PSRs) 2017, the payer’s payment service provider must be clear and upfront about conversion charges.
- PSPs must inform customers of the estimated currency conversion service charges for credit transfers before the payment transaction. They must do so in a clear, neutral, and comprehensible manner.
- PSPs must show charges in the form of a percentage markup (e.g., 2.5%) over the euro foreign exchange reference rates issued by the European Central Bank (ECB).
- PSPs must also publish the percentage marking on an electronic platform (e.g., their websites and mobile banking apps).
In other words, you should know the total amount of a transaction up front so you can make informed decisions about how to send or receive money across borders.
Traditional providers won’t always offer this information, however. Some financial firms fail to clearly display transaction fees, possible additional fees, or the fact that fees may vary, according to FCA research.
Choosing a payment solution that clearly outlines fees is crucial for understanding payments and effectively managing your finances.
We’ll talk more about payment technology soon. First, let’s look at how the UK’s position on cross-border payments can affect your business.
The Real-World Challenges of the Cross-Border Payments Regulation on UK Businesses
If you have customers in Europe or plan to expand into the EU, the change in cross-border payment rules can impact your business in two ways:
1) Daily Operational Challenges
Since leaving the EU, UK businesses face new frictions in how cross-border euro-payments are priced.
Rule amendments create challenges such as:
- Higher transaction costs. Banks now treat euro payments as international transfers. What used to be low-cost transactions can now incur varying transfer, FX, and payment card fees, adding extra complexity to routine supplier payments.
- Slower payment processing times. SEPA payments still link the UK to European accounts, but EU banks aren’t required to treat them as domestic. Some transfers are processed through the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT), which adds extra steps and potential delays.
- FX markups. Many high-street banks factor 2%–4% or more into exchange rates, plus transfer fees, making each transaction more expensive than it can initially appear.
- Less financial predictability. Banks across different jurisdictions applying varying fees and timelines make it harder for finance teams to forecast costs and reconcile payments. Inconsistency can delay payments and affect cash flow, especially for SMEs operating on tight margins.
2) Strategic Challenges
Beyond higher transaction costs and slower transfers, cross-border payment changes pose strategic implications, including:
- Pricing complexities. Volatile FX rates and new transaction fees make it harder to set stable euro pricing. Companies must decide whether to adjust their business model to absorb costs or change point-of-sale prices for each market. Otherwise, they risk passing costs on to partners or customers and compromising relationships.
- Expansion uncertainty. New friction in cross-border payments can slow EU market entry. Unpredictable costs or compliance uncertainty can make expansion less viable or appealing.
- Greater financial risk. Currency fluctuations and fragmented banking relationships introduce financial and operational risks. Without standardised controls, small errors can cause issues across regions.
- Complex tech and partner management. Businesses must ensure payment systems, banks, and tech partners can scale globally and remain compliant. Otherwise, they risk costly inefficiencies and regulatory gaps.
In short, traditional banks have made post-Brexit payments slower, more costly, and more complex for payment service users.
Because cross-border payments now behave more like international transfers than EU domestic ones, UK businesses need payment infrastructure built for multi-currency predictability, SEPA efficiency, and compliance by design.
In this scenario, mass payment automation is essential, not optional.
How Tipalti Simplifies Cross-Border Payment Management
Software like Tipalti is helping UK businesses manage cross-border payments in one system, from supplier onboarding to payouts and reconciliation.
Rather than navigate complex bank fees and conversion rates with regional banks, finance automation software simplifies processes.
From a single virtual payer’s account, you can automate global payments in multiple currencies, with locked-in FX rates, and payment methods that suit supplier preferences.
Tipalti helps UK finance teams regain predictability post-Brexit by locking in FX rates, standardising fees, routing euro payments through SEPA when possible, and providing visibility across all EU payout methods.
Making cross-border payments more efficient reduces payables time, cuts payment errors, and speeds up financial close.
Tipalti Customer Case Study
Independent music label Ninja Tune implemented Tipalti Mass Payments to automate royalty payments to its growing global roster of artists.
After struggling to manage cross-border payouts, Ninja Tune’s small team used automation to reduce their manual admin workload, eliminate bottlenecks, and ensure timely, accurate payments.
The result? A 50% faster payment cycle, earlier artist payouts, and a smoother, more transparent process that has strengthened relationships.
With Tipalti, our royalty payments not only happen faster, but it has also helped reduce the pressure on our team and may have delayed or removed the need to increase headcount.
Dawn Dobson, CFO, Ninja Tune
A more efficient process reduces cross-border payment costs and frees up time for finance teams to focus on strategic tasks like nurturing cross-border relationships.
In the next section, we’ll look at how your UK business can improve cross-border payments operations, and how automation software can help.
Automate AML and Sanctions Screening at Scale
Tipalti’s global payment automation screens every payee and transaction automatically, helping you meet AML, KYC, and sanctions requirements without slowing down payout operations.
How to Optimise Cross-Border EU Payments
To improve cross-border payments efficiency, combine smart processes with the right mass payment technology.
Streamlining your workflows and utilizing automation to manage payments helps you reduce payment costs, expedite transfers, and gain greater control over your cash flow.
Here’s how to optimise your cross-border payment process and maintain healthy relationships with EU suppliers.
Use a SEPA-Friendly Cross-Border Payment Solution
While the UK is no longer part of the EU, it participates in SEPA as a non-EU country. By making euro payments through the SEPA system, you can enjoy fast processing and fees comparable to domestic payments.
Routing payments through a finance automation SEPA solution rather than a traditional bank also lets you avoid unnecessary SWIFT fees and ensure predictable, upfront costs.
Here’s what to look for in a SEPA-friendly payment solution.
| Feature | Why It Matters | What to Look For |
|---|---|---|
| SEPA access | Ensures you treat euro payments as local, not international transfers. | The provider should support SEPA Automated Clearing House (ACH) and ISO 20022 XML compatibility for prompt payments. |
| Transparent FX rates and currency conversion services | Hidden exchange markups can harm profit margins. | Real-time foreign exchange rates with efficient conversions and clear fees. |
| Single bank account | Eliminates the need to maintain regional bank accounts for payouts. | A central virtual account to manage payments across subsidiaries, currencies, and payment methods. |
| Speed of transfer | Faster settlements improve supplier trust and cash flow. | Instant or same-day euro payments within SEPA zones. |
| Multi-currency support | Simplifies managing payments across the EU and global markets. | Ability to hold and send in multiple currencies (e.g., GBP, EUR, SEK, DKK, PLN, etc.). |
| Compliance and security | Essential for meeting UK regulatory standards, protecting against fraud, and ensuring accurate payments. | A regulated provider with robust due diligence, tax compliance, and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) features. |
Tipalti integrates with SEPA to process payments quickly and cost-effectively via global ACH from a single payout API.
It also supports global payments to over 200 countries and territories in 120 currencies, so finance teams can handle SEPA and non-SEPA transactions in one place.
Additionally, Tipalti’s features extend to payment and invoice management, including:
- Automated International Bank Account Number (IBAN) or Bank Identifier Code (BIC) validation to reduce payment delays or rejections.
- Real-time FX visibility with lock-in rates and no hidden markups.
- End-to-end audit trails for compliance with HM Revenue & Customs (HMRC) reporting requirements.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) integration to reconcile cross-border payments instantly in your accounting system.
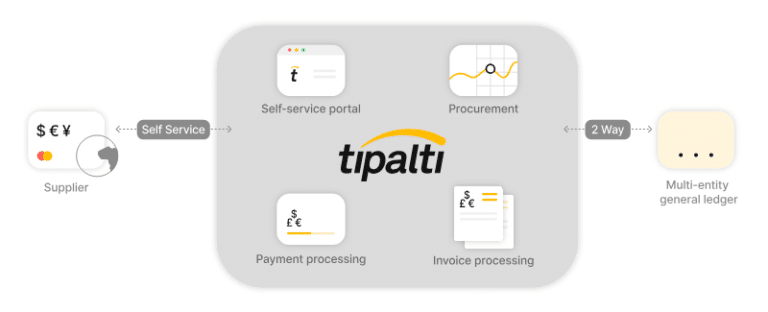
With a central hub to simplify cross-border transactions, you’ll gain payment speed, clarity, and reliability in your process — qualities that have been harder for UK businesses to achieve post-Brexit.
Batch and Automate Payment Transfers
To keep cross-border payouts low, group payment orders wherever possible.
Rather than sending dozens of small transfers individually, consolidating mass payouts into fewer larger transactions will reduce per-transfer fees and the administrative costs of managing multiple payments.
Payment automation takes this a step further, allowing you to schedule payments and establish payment thresholds.
Say you run an e-commerce business that pays EU-based affiliates a percentage of sales they make for promoting your product in their content.
Instead of crediting your affiliates’ accounts every time they earn a few euros, a mass payments solution like Tipalti lets you set up a threshold.
You can use this to:
- Hold payments until earnings reach a minimum amount (e.g, €500).
- Automatically send the bulk payment to the creator’s bank account in the correct currency when they reach the threshold.
Fewer payment transfers result in lower cross-border fees, reduce manual work, simplify bookkeeping, and enable better cash flow management.
The key to successful payment automation starts with supplier onboarding. Collecting accurate information from payees prevents payment delays or errors. It also ensures accurate records for VAT returns.
Tipalti’s self-service onboarding simplifies this process with a step-by-step approach that lets suppliers enter their business, VAT, and payment information.
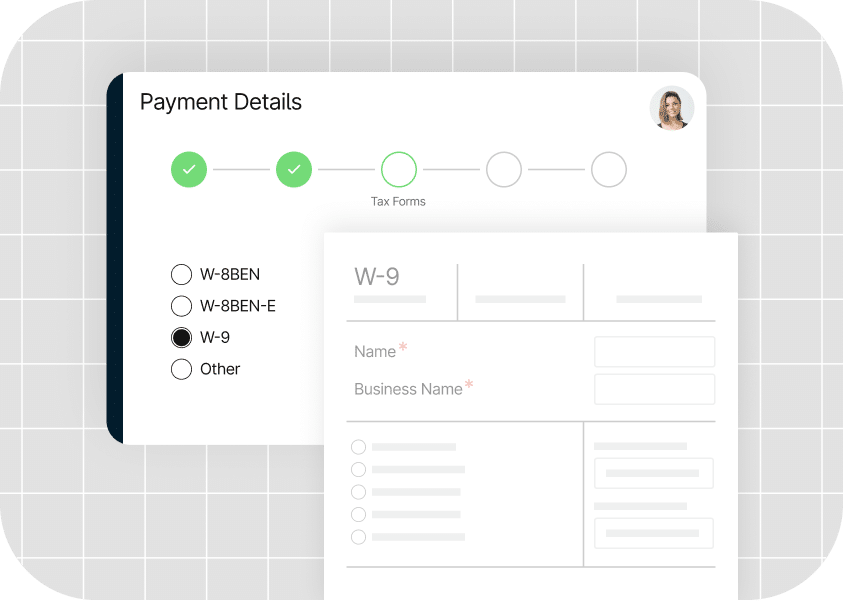
Once details are validated, Tipalti syncs authentication in your ERP system and allows suppliers to manage information, submit invoices, and track payments from within their secure Supplier Hub.
By verifying and validating suppliers up front, you promote efficiency, ensure compliance, and minimise risk across your cross-border payment process.
Understand your Cross-Border Payment Obligations
Cross-border payments are subject to a range of financial regulations that aim to protect individuals and businesses against money laundering, fraud, and privacy breaches.
While these don’t directly relate to the CBPR, understanding your obligations is essential to maintain trust and avoid penalties when managing EU transactions.
Here are the key regulations and frameworks to be aware of.
| Obligation | What It Means | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Money Laundering Regulations 2017 | Businesses and financial institutions must detect and prevent suspicious activity that could involve money laundering or terrorism financing. | You need a system that verifies customer identities, detects high-risk transactions, and reports suspicious activity to competent authorities. |
| Know your customer (KYC) | Relates to money laundering regulations. Information requirements involve verifying the identity and address of suppliers before processing payments. | Ensures you only transact with legitimate parties to prevent fraud. |
| Funds Transfer Regulation (FTR) | PSP must include detailed payer and payee information in every electronic transfer. | While it applies to PSPs, UK businesses need to provide accurate data to process payments and meet AML standards. |
| Sanctions screening | Relates to money laundering and KYC rules. Businesses must compare entities and transactions against sanction lists (e.g., UNSC or OFAC) to prohibit illicit payments. | Ensures you meet regulatory compliance and mitigate risk. Breaching sanctions can result in fines and reputational damage. |
| Payment Services Regulations 2017 (PSRs 2017) | Online marketplaces and booking services must ensure payment processes follow strong authentication rules and provide clear payment information when sending or receiving funds. | Maintains payment security, transparency, and customer protection post-Brexit — aligning with EU Payment Services Directive 2 (PSD2) standards. |
| HMRC VAT reporting | Businesses must accurately report cross-border transactions in VAT returns. | Ensures UK tax compliance and prevents penalties for unreported or misclassified transactions. |
| The Platform Operators Regulations 2023 | Online platforms must collect, verify, and report seller and income data to HMRC for transparency and tax compliance. UK DRR is the UK equivalent of the EU’s DAC7 regulation. | Ensures income earned via digital platforms across borders is properly reported and taxed, avoiding compliance risks and penalties. |
| General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) | Businesses should use platforms that securely collect, store, and transfer personal data to protect against cyber attacks and other threats. | Non-compliance can lead to fines and loss of supplier trust. |
To simplify compliance, choose a cross-border payment solution that validates and verifies suppliers and syncs accurate payment information to your ERP.
Tipalti safeguards you from the start with built-in global payment intelligence and fraud prevention features.
Adhering to your obligations helps build trust and resilience, protecting your business against penalties while creating the kind of operational transparency partners expect.
Standardise Your Cross-Border Payment Workflows
Standardising your payment workflows creates a consistent process for all suppliers, regardless of location or currency.
It eliminates confusion, reduces compliance risk, and gives finance teams more visibility and control over global payments.
We’ve already touched on automating payments and supplier onboarding. Implementing mass payments software for these processes will give you a repeatable framework.
Extending this efficiency across your entire payment process will help keep operational costs predictable as your business grows.
Here are some best practices to create a consistent workflow, along with explanations of how a payment automation tool like Tipalti promotes continuous improvement.
| Best Practices | What To Do | How Tipalti Helps |
|---|---|---|
| Create tiered approval rules | Define clear approval thresholds by payment size or region to ensure fast, consistent, auditable authorisation. | Configure custom multi-level approval workflows that automatically route invoices and payments based on value or department. |
| Centralise communication | Keep all payment-related communication and records in one place to reduce confusion and improve traceability. | Tipalti provides a unified platform that stores invoices, supplier details, interactions, and payment histories together, then syncs them to your ERP for full visibility. |
| Provide transparent remittance information | Give suppliers details on gross amounts, fees, FX rates, and net amounts received. | Automatically send detailed remittance information to the Supplier Hub, giving suppliers visibility into fees and final amounts in their local currency. |
| Monitor and lock in FX rates consistently | Establish a consistent FX strategy (e.g., fixed-rate schedules or hedging) to protect margins and simplify forecasting. | Get competitive FX rates and detailed insights to manage fluctuations and costs, minimising the impact of sudden currency movements. |
| Regularly review and update workflows | Conduct quarterly reviews of payment processes to reflect regulatory or operational changes. | View detailed spend analysis and audit trails, making it easy to identify bottlenecks and adapt workflows as your business evolves. |
Standardising and automating your cross-border payments process gives finance teams the structure to manage multiple currencies, jurisdictions, and suppliers in one place.
When you’re not dealing with regional banks and fragmented transactions, EU and global payments become more transparent and financially viable, even as you scale.
Cross-Border Payments Regulations FAQs
How does the Cross-Border Payments Regulation impact international business transactions?
The Cross-Border Payments Regulation affects euro payments within the EU. For UK businesses, transactions with suppliers inside and outside the EU are not directly covered. Fees, FX costs, and processing times are set by banks or payment providers. Making payments to global suppliers requires an efficient approach to control cost and risk.
What’s the difference between SEPA and SWIFT payments?
SEPA (Single Euro Payments Area) facilitates euro payments within the EU and a few partner countries. It’s fast, low-cost, and often treated like a domestic transfer. SWIFT is a global electronic message system for sending money internationally in any currency, but transfers can be slower and involve multiple banks. Use SEPA for euro payments to EU accounts to save time and fees. Use SWIFT for payments outside the euro area or in non-euro currencies.
How do new Cross-Border Payments Regulations impact the speed and cost of cross-border EU payments?
Since Brexit, the EU CBPR no longer applies, meaning cross-border payments between the UK and the EU can be slower and more expensive. Banks can charge international transfer and FX fees, and some EU banks route payments via SWIFT instead of SEPA, adding time and cost. Tipalti helps restore faster, affordable transactions with a central account, lockable and competitive FX rates, and multi-currency support.
What global payment methods does Tipalti support?
Tipalti’s global payout platform supports efficient cross-border payments to 200+ countries and territories in 120 local currencies, using 50+ payment methods, including local bank transfers such as SEPA and BACS, Global ACH, PayPal, and wire transfers (e.g., SWIFT).
What industries is Tipalti mass payments best for?
Tipalti’s cross-border payments features are ideal for online platforms, including marketplaces, adtech, gaming, content platforms, and gig economy companies that make global payouts.
Simplify Cross-Border Payments with Tipalti
Brexit has made cross-border payments to the EU more challenging for UK businesses, but traditional banks aren’t your only option. By streamlining your workflows and selecting a SEPA-compliant automation solution, you can reduce fees, enhance transparency, and maintain control over your international payments.
See how Tipalti Mass Payments helps you manage cross-border payments and operate in new markets without compromising efficiency or compliance.
