Businesses use accounts payable aging reports automatically generated by their accounting software to manage accounts payable balances, identify early payment discounts, and know when payments to their suppliers offering credit terms are due.
What is an Accounts Payable (AP) Aging Report?
An accounts payable aging report is a critical accounting document that summarizes the bills and invoices owed by a business, broken down by vendor and due date. It shows columns with amounts grouped into Current, ranges for the number of days past due, and a Total amount column. A detailed AP aging report shows invoices with reference number, due date, payment terms, and balance due. The opposite of accounts payable aging report is an accounts receivable report, which outlines when a business can expect payment from their customers.
Understanding Accounts Payable Aging Reports
Understanding accounts payable aging reports requires knowing how much your business owes its trade creditors (vendors or suppliers offering credit terms), what payment terms mean, early payment discounts offered, and when the invoices are due or past due. You should also understand the relationship between the accounts payable aging report and cash flow.
The AP aging report, which applies to vendor invoices for purchases, is similar to the accounts receivable aging report that determines the balance due of open (not yet collected) customer invoices.
How do you Prepare an Accounts Payable Aging Report?
The process of how to prepare an accounts payable aging report includes: categorizing and summarizing totals for unpaid supplier invoices by each vendor name and invoice (in the detail), with columns for Current amounts (not past due), at least 30-day increments of the number of days the payables invoices are past due, and Total.
Because the AP aging only includes invoices with credit terms on account, bills paid immediately by credit cards, cryptocurrency, or cash payment methods aren’t included in the accounts payable aging report.
Accounting software and ERP systems provide the functionality to generate accounts payable aging reports automatically each month as a detail report and summary report.
The accounting system considers vendor invoice amounts, credit memos or debit memos issued, and any partial payments to compute the remaining balance due to each vendor. If your company takes an early payment discount, the accounting software will remove the entire invoice amount from the accounts payable aging upon payment.
Small businesses may want to use Excel template spreadsheets to prepare an accounts payable aging report manually. But it isn’t efficient or recommended. Excel AP aging preparation could result in missing vendor invoices in the aging report or incorrect vendor invoice numbers, due date information, and calculation errors.
To ensure financial reporting and accounts payable completeness at each month-end, record vendor invoice amounts relating to the accounting period through the monthly cut-off date (after the end of the month) in the system or initially as an accrual journal entry for accounts payable. Reconcile the accounts payable aging report details to vendor statements and the general ledger balance for accounts payable. The AP aging is a journal reflecting recorded accounting transactions for accounts payable.
Correct any accounts payable recording errors with journal entries. After making corrections, run a final accounts payable aging report for the month-end date.
The CPA firm auditing or reviewing your company’s financial statements will ensure that balance sheet account reconciliations are regularly completed for adequate bookkeeping, business accounting, and internal control.
What Information is Included in an Accounts Payable Aging Report?
A summary accounts payable aging report shows totals by each vendor with outstanding (unpaid) invoices billed to the business purchasing services or products of any type, including inventory and supplies.
A detailed accounts payable aging report lists the yet unpaid balances of invoices owed to each supplier. Each invoice line shows invoice number, invoice date, payment terms, and due date information based on the payment terms. It may also indicate the purchase order number (PO number) or another type of document reference number like a credit memo number associated with the invoice.
The first column is Vendor Name.
Accounts payable aging report column titles for current, past-due aging ranges, and total are:
- Current
- 1 – 30 days
- 31 – 60 days
- 61- 90 days, and
- Over 90 days
- Total
The number of days ranges are the number of days past due based on the invoice date and credit terms. The Current column shows by-vendor totals of the newest invoices with unpaid balances that aren’t past due for payment yet. The AP aging report may show columns for 91 – 120 days and over 120 days columns instead of the column for over 90 days.
In each applicable aging column, the total amount of the balance of the invoices due is shown for each applicable days outstanding range. A summary AP aging report only includes total amounts owed by vendor name. The detail report also shows line items for each invoice within a vendor grouping, with related invoice balance due amounts by current, past-due age range, and total. The detailed AP aging report shows rows with subtotals by vendor name.
An accounts payable aging report includes the total for all vendor amounts owed and by column for each aging date range, using current and days past due date ranges. Totals are shown by column on the bottom of the aging report and in the rightmost Total column that calculates the total of all days outstanding range columns.
Example of an AP Aging Report
An example of an Accounts Payable Aging Report Summary is shown as of month-end. With modern accounting systems, you can run an accounts payable report daily or anytime on-demand to manage your company’s accounts payable and required payments.
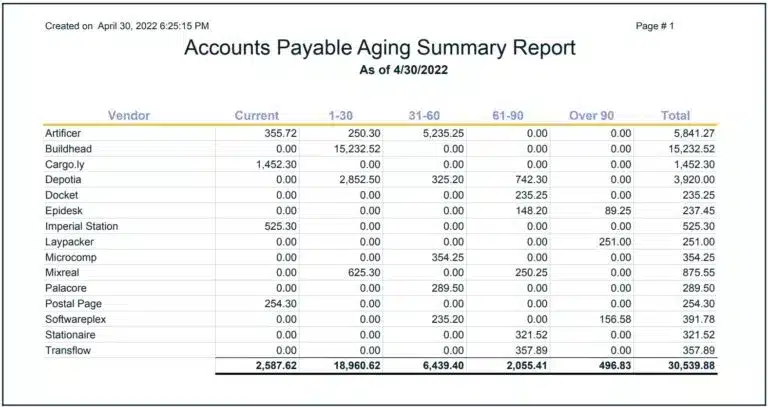
How Do You Read AP Aging Reports?
Read AP aging reports by looking at the total balances due that are current or by the date range of days past due to determine approximately when your business needs cash to pay vendors or the extent of past due invoice amounts owed to vendors. Pay attention to dates for earning early payment discounts.
Then focus on invoice balances owed to each vendor in the detailed AP aging report. Do the vendor names look reasonable for your business needs? Search for duplicate invoices and negative balance due amounts shown for a vendor. If the report is accurate, decide whether to request a vendor refund for these negative balances.
What 3 Transactions are Reflected in the Accounts Payable Aging Report?
The accounts payable aging report reflects 3 types of transactions in the calculation of outstanding accounts payable balances requiring payment:
- Vendor bills invoicing your business as a customer for purchases
- Vendor credit memos (for returned or damaged items or price corrections), and
- Invoice payments made to vendors
Aged Payables Report vs. Accounts Receivable Aging Report
The difference between the aged payables report vs. accounts receivable aging report is vendor invoice vs customer invoice. The AP aging report reflects the total of unpaid invoice balances due by vendor and current amounts or the number of days past due in 30-day ranges. The AR aging report shows amounts for customer invoices billed with credit terms but not yet collected.
Benefits of AP Aging Reports
Benefits of AP aging reports include:
- Ability to review the report before payment for possible errors like duplicate invoices
- Plan and schedule vendor invoice payment dates for cash flow timing and needed financing
- Save money by Identifying early payment discounts and avoiding late payments penalties
- Use to forecast accounts payable balances and cash flow in your business plan
- Achieve greater accuracy by reconciling AP aging vendor balances with vendor statements received and general ledger
Importance of AP Aging Reports
AP aging reports are important for: planning cash flow and required financing, scheduling vendor payments to pay bills per company policy, taking early payment discounts to save money, avoiding late payment penalties, and identifying and investigating reasons for past due accounts payable to vendors.
When establishing the company policy for setting vendor invoice payment dates for your company, a company should consider its accounts receivable collection time (days receivable outstanding, DRO) compared to days payable outstanding, DPO.
The accounts payable aging report is a useful tool to identify incorrect vendor invoices to be reissued upon correction, disputes, vendor product quality issues, and your company’s potential cash flow problems. Significant cash flow issues could result in a vendor’s bad debt or harmful new product shipment delays or stops for your business.
