
See how forward-thinking finance teams are future-proofing their organizations through AP automation.
Companies of all sizes use enterprise risk management (ERM) to assess strategies, reduce significant downside, and improve business performance. A COSO ERM framework provides the rationale and guidance for implementing an enterprise risk management program.
Enterprise Risk Management Defined
Enterprise risk management (ERM) is a framework for processes implemented throughout the organization. Management and the Board of Directors use ERM when considering business strategies and optimizing performance. ERM determines risk appetite, assesses riskiness of possible strategic initiatives, and reduces negative impacts of potential events or uncertainties for selected growth opportunities.
Enterprise Risk Management Includes
Enterprise risk management includes:
- Comprehensive risk assessment at the entity and corporate level
- Board of Director and management involvement
- Corporate culture, mission, and core values
- Getting input from throughout the organization
- Using advanced analytics and data visualization
- Using risk as a factor in strategic decision-making and project selection
- Implementing internal controls
- Cybersecurity and data protection
- Adequate insurance to mitigate risk
- Providing risk disclosures to stakeholders
To increase stakeholder transparency, publicly traded companies disclose material (significant) enterprise risks from internal and external forces in their 10-K annual reports. Types of risks encompass internal and external risks, including competitive, geopolitical, supply chain and vendor risks, environmental, foreign exchange risks, and other related risks.
The SEC proposed a mandate in its climate change disclosure rule for all public companies on March 21, 2022. The rule covers risks businesses face from climate change and reporting of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. The SEC rule changes could be implemented in fiscal 2023 for large companies and fiscal 2024 for smaller companies (unless a court challenge delays implementation).
Advanced analytics and data visualization help companies gather business intelligence to assess emerging risks and monitor risk exposures. These technologies can provide key risk indicators as dashboard metrics. Artificial intelligence and automation provide valuable insights that might not otherwise be discovered.
Enterprise Risk Management Framework
COSO, the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission, updated its Enterprise Risk Management framework in 2017, renaming it Enterprise Risk Management — Integrating with Strategy and Performance. The original Enterprise Risk Management — Integrated Framework it replaces was issued by COSO in 2004. COSO provides a free Executive Summary of the 2017 Enterprise Risk Management framework on its website.
COSO’s 2017 Enterprise Risk Management framework lists and describes five components of enterprise risk management.
Components of Enterprise Risk Management
The components of enterprise risk management (updated by COSO in 2017) are:
- Governance & Culture
- Strategy & Objective-Setting
- Performance
- Review & Revision
- Information, Communication, & Reporting
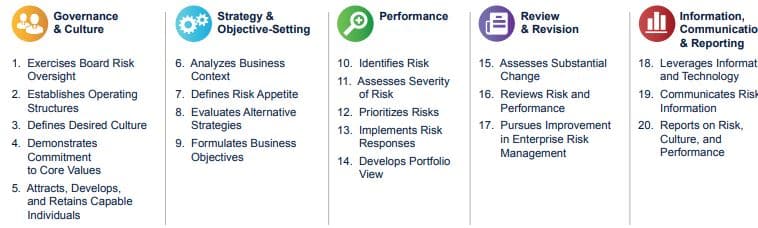
Image Source: COSO Executive Summary: Enterprise Risk Management — Integrating with Strategy and Performance (2017)
These five components are supported by a set of fundamental principles, spanning the range of practices from governance to monitoring.
The Board of Directors and senior management are responsible for the oversight of risks and performance, corporate governance, and maintaining a positive culture that can contain risks. “Culture pertains to ethical values, desired behaviors, and understanding of risk in the entity,” according to the COSO ERM framework.
Strategies derived from strategic planning should align with an organization’s mission, vision, and core values. Organizations need to assess their strategic risks and performance and the implications of strategies chosen. The company formulates appropriate business objectives combined with strategy setting.
Performance processes include risk assessment in relation to risk appetite, prioritization of risks, selecting risk responses, and reporting to stakeholders. Performance includes assessing and monitoring operational risks.
Review & revision is a process to assess substantial change, review significant risks and business performance, and determine where applying enterprise risk management components requires change.
Information, communication, & reporting is obtaining and sharing internal and external information throughout the organization in all directions, with adequate communication and reporting.
Goals of Enterprise Risk Management
The goals of enterprise risk management are to incorporate risk assessment and mitigation into a company’s corporate governance and management processes and implement it throughout the organization. Using a rigorous ERM process that follows the COSO framework, businesses can minimize surprises and enhance their growth and performance while keeping stakeholders informed.
Enterprise risk management is used in strategic decision-making and tactical implementation. Enterprise risk management helps a business set worthy business and strategic objectives, fenced in by an acceptable risk appetite level. ERM monitors and reduces internal and external risks facing the organization.
Enterprise risk management helps a company anticipate, detect, and respond to change. Risk assessment includes potential risks, new risks, and changes to existing business risks. Change creates both threats requiring lessening of downside risks and lucrative opportunities to pursue. ERM methodology builds resilience.
Importance of ERM
ERM (enterprise risk management) is important because it’s used by companies to perform a risk assessment of growth strategies being considered and current operations. When enterprise risk management is implemented throughout the organization, it can reduce surprises and improve business results, including profitability and cash flow. ERM improves the corporate governance and oversight process.
ERM helps companies reduce the variability of results and deploy resources optimally to improve performance.
Concluding Thoughts
COSO, the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission, issued an ERM framework, Enterprise Risk Management — Integrating with Strategy and Performance (2017). This ERM framework incorporates the COSO Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013). As part of internal control, enterprise risk management includes cash controls.
Enterprise risks include strategic, operational, and financial risks for companies of all sizes.
As a current or aspiring member of company management or a Board of Directors, you need to recognize that enterprise risk management is essential to your fiduciary duty for corporate governance and oversight.
Equally important, enterprise risk management can positively impact business units and corporate results as one driver of competitive advantage. ERM helps you protect business stakeholders and reward investors with fewer surprises and optimal business results in the current risk environment. You can apply enterprise risk management concepts to enhance your business contributions.
When the enterprise risk management framework is effectively implemented, the benefits of the enterprise risk management process greatly exceed the costs.