What is a Bank Code?
A bank code (ABA routing transit number) is a nine-digit number identifying bank or credit union routing and account numbers in the U.S. The bank code format varies internationally.
Common uses of bank codes:
- Electronic Payments or Deposits (EFTs)
- ACH Transfers (one-time or recurring)
- SEPA Payments (in the EU)
- Wire Transfers
- FedNow and RTP Instant Payments
- Checks
Bank codes are also used for:
- Bank Account Deposits
- Online Payments
- Direct Deposits
- In-Branch Transactions
Key Takeaways
- Bank codes are standardized formats used to transfer money domestically and internationally.
- Bank codes identify financial institutions and account numbers.
- Examples of bank codes are ABA, IBAN, SWIFT, CLABE, and IFSC.
- Bank codes are crucial for global payments, facilitating secure and efficient cross-border transactions.
Different Types of Bank Codes
Major types of bank codes used in the U.S. or internationally include:
- Routing number (ABA number) and bank account number
- IBAN
- SWIFT code (SWIFT/BIC)
- CLABE
- Sort Code
- BSB (in Australia)
- New Zealand BSB/Clearing Code
- IFSC
- MICR Code (in India)
- Hong Kong Bank Code
- Zengin Code (in Japan)
Bank Codes by Country
The following table (which is not all-inclusive) summarizes the use of bank codes by country:
| Country | ABA | SWIFT | IBAN | IFSC | Domestic Use | International Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Yes | Yes | No | No | ABA (ACH, wire transfers, checks) | SWIFT for international |
| Canada | No | Yes | No | No | Transit/Institution codes | SWIFT for international |
| United Kingdom | No | Yes | Yes | No | Sort Code + Account Number | IBAN + SWIFT for international |
| Germany | No | Yes | Yes | No | IBAN for domestic & SEPA | IBAN + SWIFT |
| France | No | Yes | Yes | No | IBAN for domestic & SEPA | IBAN + SWIFT |
| India | No | Yes | No | Yes | IFSC for NEFT/RTGS/IMPS& MICR Code | SWIFT for international |
| Australia | No | Yes | No | No | BSB Code + Account Number | SWIFT for international |
| Brazil | No | Yes | No | No | Bank Code + Branch + Account | SWIFT for international |
| Mexico | No | Yes | No | No | CLABE for domestic | SWIFT for international |
| United Arab Emirates | No | Yes | Yes | No | IBAN for domestic | IBAN + SWIFT |
| South Africa | No | Yes | No | No | Branch Code + Account | SWIFT for international |
| Singapore | No | Yes | No | No | Bank Code + Branch Code | SWIFT for international |
| Japan | No | Yes | No | No | Zengin Code | SWIFT for international |
| Switzerland | No | Yes | Yes | No | IBAN for domestic & SEPA | IBAN + SWIFT |
| Netherlands | No | Yes | Yes | No | IBAN for domestic & SEPA | IBAN + SWIFT |
1. Routing Number
In the United States, the bank code for financial transactions combines a routing number and a bank account number. The external bank identification routing number and bank account number are printed in MICR ink on the bottom of each check, with the routing number to the left of the bank account number.
The check number is to the right of the routing number and bank account number. MICR is magnetic ink character recognition, used by computers to read the numbers automatically.
Example of account and routing bank code numbers:
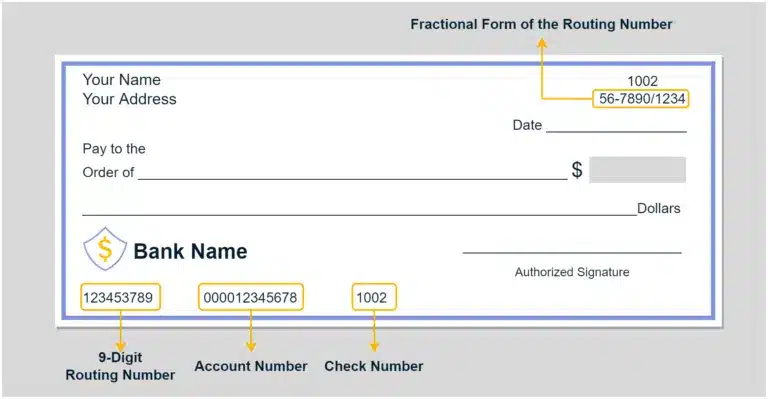
The routing number is also printed on the top right of the check, in a different format shown as a fraction. The fraction format is used as a backup number to process checks if the MICR printing can’t be read.
The internal routing number for a bank on a deposit slip is also printed in MICR as a different number.
Simplify global payments with confidence
Sending cross-border payments shouldn’t be complicated. With Tipalti, you can streamline global transactions using verified bank codes like SWIFT, IBAN, and ABA—ensuring accuracy, speed, and compliance every time.
2. IBAN
IBAN (international bank account number) is a standard format bank code of up to 32 alphanumerics used internationally (but not in the U.S. or Canada) to identify a foreign bank account and make wire transfers and interbank transfer transactions, including cross-border payments. The IBAN number includes a country code, two check digits, bank identifier code, branch code, and a bank account number.

Countries using IBAN include all EU countries, the UK, Middle East, Africa, Pakistan, Latin America, and Caribbean countries.
The IBAN-using countries list, which may not be all-inclusive, includes the following:
- European (EU) countries
- United Kingdom (UK)
- Middle East:
- United Arab Emirates (UAE)
- Saudi Arabia
- Qatar
- Bahrain
- Iraq
- Jordan
- Kuwait
- Lebanon
- Libya
- Israel
- Some African countries
- Pakistan
- Latin America:
- Brazil
- Costa Rica
- El Salvador
- Guatemala
- Caribbean:
- Dominican Republic
- Saint Lucia
- Other islands
3. SWIFT Code
A SWIFT code is used worldwide for money transfers between banks for international transactions. The SWIFT code or Bank Identifier Code (BIC) is an eight to 11-digit code of alphanumerics to identify the bank, country, the bank’s head office location, and optionally a specific branch.
4. CLABE
In Mexico, CLABE (Clave Bancaria Estandarizada) which translates to standardized bank code or standardized bank cipher, is used for 18-digit Mexican bank account numbers. The CLABE is used for banking transactions, including bank transfers.
5. Sort Code
The Sort code is used in England and Ireland as a bank code to identify the bank location of a bank account. Sort codes are six digits, expressed as three sets of two numbers separated by a hyphen. The Ireland sort code, also referred to as National Sort Code or NSC, begins with 9.
The sort code is used as part of the IBAN code for making bank transfers internationally.
6. BSB (in Australia)
The BSB (Branch State Bank) code is used as a bank branch identifier in Australia. The BSB code consists of six numbers, with the first two or three digits for branch identification. In Australia, international bank transfers use a BSB, account number, and SWIFT code (the same as a BIC code) for processing through the SWIFT network.
The BSB code, the location code for a specific bank branch, is on a bank statement and online banking account. The BSB number can be found by searching a BSB branch locator on your bank’s website or another online BSB checker tool.
7. New Zealand BSB/Clearing Code
New Zealand uses its own six-digit BSB bank code to identify a bank (first two digits) and specific branch location (last four digits) of a financial institution in that country. To make a wire transfer, you also need the seven-digit account number and the suffix of two or three digits.
8. IFSC (in India)
In India, the IFSC (Indian Financial System Code) is used as a bank code to transfer money within India between banks and to transfer foreign money to Indian bank accounts. IFSC is an 11-digit alphanumeric code used for electronic fund transfers.
9. MICR Code (in India)
Besides the IFSC, India also uses a MICR code for using an Electronic Clearing System for check processing. The MICR code consists of City Code, Bank Code, and Branch Code of three digits each, totaling nine digits. MICR is magnetic ink character recognition printing on checks for automatic electronic reading.
10. Hong Kong Bank Code
The Hong Kong bank code is a three-digit bank code number only used for domestic bank account transactions within Hong Kong to identify the bank name. It’s combined with the branch code and bank account number to make bank transfers.
Hong Kong also uses the SWIFT code and IBAN for making overseas bank transfers.
11. Zengin Code (in Japan)
The Zengin Code used in Japan for domestic transfers has seven digits, with a four-digit bank code and a three-digit branch code. Zengin Code is also used for PayPal and Google Adsense online payment transactions.
The Role of Bank Codes in Global Payments
Bank codes, such as SWIFT, IBAN, and ABA, are essential in simplifying global payments, with the role of standardizing bank routing and accounts for making domestic and international cross-border payments.
The Value of Global Cross-Border Payments and Initiatives
In his May 6, 2025, keynote at the Asian Development Bank (ADB) Annual Meeting, Fabio Banetta stated that the global cross-border payments market reached $190 trillion in 2024 and is projected to exceed $300 trillion in the next 5–10 years.
Banetta also highlighted Italy’s 2024 objectives for enhancing cross-border payments, focusing on the creation of bilateral interlinking arrangements between payment systems, a key initiative under the BIS Roadmap.
The Bank for International Settlements (BIS)—which supports global monetary and financial stability through international cooperation—has been instrumental in driving these improvements to modernize global payment networks.
ISO 20022 Adoption
The ISO 20022 standard will be adopted worldwide by November 2025 as a unified global payment standard, modernizing financial transactions through enhanced data exchange.
Organizations, including financial institutions with BICs for SWIFT transactions and FedNow, will leverage ISO 20022 to streamline processes. Corporations, market infrastructures, and securities market participants may also adopt ISO 20022, although they can choose to retain ISO 15022.
How Automation Streamlines Global Payments
Automation technology plays a crucial role in simplifying global payments by efficiently managing complex processes. With automated systems like Tipalti, businesses can streamline payee and supplier onboarding through self-service portals that securely collect contact information, preferred payment methods (including bank codes), and necessary tax forms before initiating payments.
Tipalti also enhances compliance by validating bank routing details—such as SWIFT and IBAN codes—to reduce errors and ensure accuracy. Additionally, global regulatory checks, like screening against OFAC blacklists based on the payee’s country and payment method, are seamlessly integrated into payment workflows, minimizing risks and maintaining compliance.
As global commerce continues to expand, mass payments automation technology remains essential for efficient, secure, and compliant cross-border transactions.
Bank Code FAQs
These FAQs answer more questions about the meaning of bank codes.
What is ABA Number?
An ABA number is a nine-digit number called a routing number or routing transit number (RTN) to identify banks and branches in the United States in a standard format defined by the American Bankers Association.
How Do You Find an Example Bank Code Routing Number in the U.S.?
To find a bank code in the U.S., refer to your bank account statement, mobile banking app, or the bank’s lookup page for routing numbers. For example, you can find the Chase routing number bank code for your area, which may vary by state or region in the United States by logging on and entering the last four digits of your bank account.
Are SWIFT Code and BIC the Same?
Yes. The SWIFT code standard format is specified in ISO 9362 as a BIC. International bank transfers go through the SWIFT network.
Where Do I Get a SWIFT/BIC Code?
The SWIFT network issues each BIC code specified in ISO 9362. Besides SWIFT code, people refer to the BIC code as bank identifier code, bank identification code, business party identifier, and business identifier code.
What are the SubCodes Within a SWIFT Code or BIC Code?
The eight to 11 alphanumeric character code for SWIFT/BIC has four parts, including the optional branch code:
1. Bank code (four letters) specifying the bank name
2. Country code (two letters)
3. Location code (two numbers up to nine or letters) to identify the bank head office
4. Branch code (three digits) for a particular bank branch location or XXX for head office) – optional
Does the U.S. Use the SWIFT Code (BIC)?
Although the U.S. has its unique ABA routing numbers for bank codes, SWIFT number codes are used in the U.S. to send international money transfers through the SWIFT network.
Do I need a bank code for wire transfers?
Yes. You need a bank code for wire transfers. U.S. domestic wire transfers require an ABA code. International wire transfers use SWIFT, IBAN, or specific country codes like IFSC in India, or routing/transit number in Canada.
Can I use IBAN and SWIFT together?
Yes, IBAN and SWIFT codes work together in international banking. IBAN is for the bank account, and SWIFT is a bank or branch identifier.
