
See how forward-thinking finance teams are future-proofing their organizations through AP automation.
Fill out the form to get your free eBook.

Today, the finance function has more responsibilities than ever. In high-growth businesses, every operation—both front and back-office—is inexplicably tied to investment versus reward. To survive the uncharted road ahead, the modern, forward-thinking finance team has to future-proof their organization for success. Download the guide to discover: – The untamed wilderness of finance – How to forge an accounts payable path – How to strategize your next move – The ultimate accounts payable survival tool – How real-life survivalists scaled their businesses
Companies use expense reports to approve and reimburse employees for their expenses incurred on behalf of the company. Businesses seeking efficiency are replacing old-style paper expense reports, receipts, and checks with automated expense management software with a mobile app or online expense report submission and electronic payments.
According to the Global Business Travel Association, it takes an average of 20 minutes to complete one expense report, costing the company $58 per transaction. But it doesn’t stop there. Added to that figure is the cost of correcting expense reports, which happens 19% of the time. So, what are the best ways to handle employee expense reports and ensure your general ledger is accurate? It starts with the right types of tools and accounting software.
Using best practices, you can learn how to use, process, pay, and record expense reports as part of the AP cycle (for accounts payable).
Expense report automation software, working with AP automation, helps your business achieve optimal spend management and business process efficiency by:
- Simplifying and digitizing the process for their employees submitting expense report claims
- Strengthening controls and global regulatory compliance
- Automating approval workflows
- Streamlining business processes
- Eliminating unnecessary steps like verifying the accuracy of employee-prepared spreadsheets, manual data entry, chasing down lost paper expense reports, and hounding approvers
This guide covers what an expense report is, its purpose, the types of expenses submitted on business expense reports, how to fill out an employee expense report, and how to create an expense policy. It explains why automation software is preferable, less costly, and faster for creating employee expense reports than spreadsheet preparation and manual processing for verification, approval, and payment.
Key Takeaways
- Businesses use an expense report with receipts to document, approve, and pay for employee expense reimbursements.
- Expense report items typically include travel expenses, business mileage, training, and professional expenses.
- These are generally business-related out-of-pocket costs charged as personal credit card transactions or paid with employees’ funds.
Types of expense report items included to create expense reports are airfare, lodging, car rentals, business travel, entertainment, meals, business mileage (with mileage tracking and calculated at the company’s or IRS-approved standard mileage rate), ground transportation, professional license fees, training courses, and office supplies.
In some circumstances, nonemployees may also be allowed to submit expense reports for reimbursement to a company.
What Is an Employee Expense Report?
Employee expense report is a method businesses use to reimburse employees for work-related expenses. An expense report includes a list of expenses incurred, the business purpose, and the date and amount of each expense.
It is a simple yet crucial step in an effective expense management system that will help you keep track of employee spending and ensure staff is only spending on behalf of the company.
The expense reporting process was created because, at times, employees must use their own money or personal vehicle for business-related tasks. Thus, it is only fair for them to receive money back and benefits like mileage reimbursement.
Different Types of Expense Reports
Different types of expense reports include:
- Travel expense reports: transportation (airfare, rental cars, gas or standard mileage, Uber/Lyft), hotels, restaurant meals or per diem expenses, etc.
- Local business mileage: standard mileage or gas receipts
- Professional expenses: professional license fees, membership dues, event fees, etc.
- Incidentals: office supplies, subscriptions, and other maverick spend
- Non-employee expenses, such as airline customer reimbursements for flight delays and cancellations
Businesses may also consider expense reports to be financial reports for expenditures that may not require employee reimbursement and attorney-billed and invoiced client expenses.
Importance of Expense Reports
Expense reports are important because they let employees receive reimbursement for valid and approved business expenses for which they will pay the supplier directly. Expense report forms are submitted with receipts as proof of spending. The company’s employee expense policy will state any minimum amount requiring a receipt (such as $20) to substantiate the amount of employee spending.
Businesses record expense reports as accounts payable that will be paid by the company upon approval. As the debit side of the entry, the accounts payable team codes the expenses to the applicable accounts, such as the travel category, auto mileage reimbursement, training courses, or professional license fees.
Companies using well-designed expense reports and expense report software can perform expense tracking for business spending by each employee, department, and project for spend analysis. Managers and businesses compare actual spending to budget amounts. Using this information, companies implement cost control during the year.
How the Expense Report Process Works
How expense reporting works is:
- Employees submit their expense reports to their employer through their accounts payable department within the finance team.
- AP verifies it and routes the expense report to their manager, who has budget responsibility for reviewing and approving the request for reimbursement.
- Once approved, the employer issues a direct deposit or check to reimburse the employee for the expense.
The first step is to ensure you have a system in place for employees to submit their expense reports. This can be done electronically or through a paper form. In the past, these types of things were managed with an Excel spreadsheet, but with the introduction of expense reporting software, the entire process has been streamlined.
Businesses require employees to include receipts or other documentation with their expense reports. This can help the finance team verify the legitimacy of the expense and ensure that the company is getting what was paid for.
Expense Report Template Example
In a business, all employees use the same expense report template selected by their company.
An expense report template might look like this:
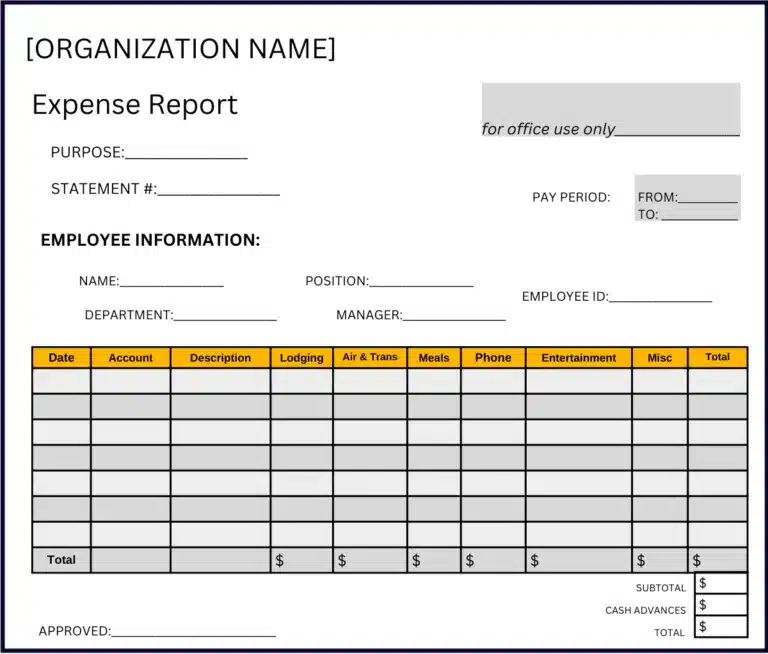
How to Fill Out an Expense Report
Steps to fill out an expense report include:
- Enter your name, department, and employee ID number as contact information.
- Date the employee expense report.
- Provide a brief description of the expense for each and the business purpose of expenses submitted for reimbursement.
- Enter the date, type, and amount of each expense in the related column.
- Attach receipts paid by credit card or cash, or submit images of receipts for each expense (or if completed manually, for expenses above the company policy threshold amount).
- Indicate any client/customer or project for which an expense was incurred, if applicable.
- Categorize and total expenses by each expense category column, for the total amount by row, and as a Subtotal in the last column.
- Subtract any cash advances you’ve received from the company.
- Calculate the balance due for expense reimbursement as the Grand Total.
- Sign the expense report (digitally for an online expense report).
The expense report is filled out by the employee and submitted to the accounts payable department through the expense reporting process. Account coding will be done or checked first. Then, the expense report will be approved (or some items on it rejected) by a supervisor, manager, or small business owner with budget authority, and finally paid.
If some expenses aren’t approved as part of the expense reimbursement amount, a revised expense report will be required for the total cost actually reimbursable, or a lesser amount will be paid after electronic communication.
Following IRS rules, only reasonable expenses with a justifiable business purpose should be approved for payment by the company as a reimbursement. Businesses don’t reimburse what they consider to be the employee’s personal expenses (that aren’t tax deductible by the business).
Qualified employees in the following categories can take employee business expense deductions for unreimbursed employee expenses. In tax season, they use IRS Form 2106, Employee Business Expenses to take the tax deduction for deductible expenses.
According to the IRS, at tax time, “qualified employees” for unreimbursed employee business expense deductions on tax returns include:
- “Armed Forces reservists
- Qualified performing artists
- Fee-basis state or local government officials
- Employees with impairment-related work expenses
No other type of employee is eligible to claim a deduction for unreimbursed employee expenses.”
Automate employee expense reports from submission to reimbursement
Tipalti Expenses, in combination with AP automation software, makes submitting and processing expense reports and reimbursing expenses more efficient than ever.
What Are the Steps in Creating an Expense Policy?
An expense policy is a set of guidelines that employees must follow when incurring business expenses. But first, what is an expense? An expense is a cost incurred by the company and its employees.
The company expense policy should include what types of expenses are covered or allowed, how to document expenses, and the reimbursement process.
Here’s how to get started.
1. Define which types of expenses are covered or allowed
The first step in creating a company expense policy is to define which expenses are eligible for reimbursement. This will help you avoid reimbursing employees for personal expenses.
Some common examples of work-related expenses that may be eligible for reimbursement include travel, business meals, business entertainment, business gifts, and office supplies.
Be as specific as possible when defining which expenses are eligible for reimbursement. This will help to avoid any confusion later on.
2. Set a limit on the amount that can be spent per category
Once you have defined which expenses are eligible for reimbursement, the next step is to set a limit on the amount that can be spent per expense category. This will help control employee spending and avoid unnecessary or extravagant expenses.
For example, you may want to set a limit of $50 per day for travel expenses, $25 per meal for business meals, and $100 per month for office supplies. These limits can be set per transaction, per month, or per year.
3. Require employees to submit documentation with their expense report
The next step in creating an expense policy is to require employees to submit documentation with their expense reports. This documentation can include receipts, invoices, or credit card statements.
Requiring employees to submit these will help you verify that the expenses were incurred and are work-related. It will also help to prevent fraud and abuse of the system.
4. Define the reimbursement process
Create a step-by-step reimbursement process to specify how and when employees will be reimbursed for their expenses. Will employees be reimbursed every month? Or will they be reimbursed immediately after they have incurred the expenses? Will you reimburse them through direct deposit or with a check? The functionality of this step is to be adamantly clear and concise about policy so all expectations are met.
Defining the reimbursement process beforehand will help avoid confusion or delays in getting employees reimbursed for their expenses.
5. Create an ethical statement
Including an ethical statement in your expense policy will help ensure that employees behave ethically when they spend company money.
Some common ethical considerations that should be addressed in the statement include avoiding conflicts of interest, being honest and transparent about expenses, and refraining from using company funds for personal gain.
6. Use an efficient reporting system
The final step in creating an expense policy is to use a good reporting system for business spending. You can start with a paper system or a simple online expense report form. But if you want to streamline the process to save time and money, you may want to consider using expense management software.
An expense management system will help you automate repetitive and tedious tasks in monitoring and processing expenses, such as verifying allowable expenses and their limits or spotting and correcting errors. It will also allow your employees to submit their expenses and documentation online.
You may also want to consider your ERP integrations and how these new policies can be implemented in other programs.
A Faster Way: Expense Report Software
Expense report software streamlines processes, providing benefits for employees and their employers. The software offers digital receipt capture, faster preparation and review, and eliminates the need for time-consuming paper expense reports. It verifies calculations and global compliance, automates approvals, and offers EFT payment via ACH bank account direct deposit into the employee’s account.
The employee may be able to choose other payment methods offered through the expense report software or automated global payments software.
Expense report software, including expense management and AP automation software, works through ERP integration to track expenses, control expenditures, and provide more functionality in a seamless way. It allows you to automatically record expense and payables transactions into your ERP system or small business accounting software through a data syncing process.
Employees may select a mobile expense report app to submit photo receipts or upload receipts to add expenses and data when filling out expense report forms.
Streamline Spend Management with Tipalti Expenses
The Tipalti platform provides a unified solution for managing accounts payable, procurement, company cards, expenses, and global remittance. Tipalti Expenses automation software helps your business achieve expense management best practices.
Tipalti Expenses is a product that automates the reimbursement process and spend control over employee expenses. Companies can quickly and easily manage all expenses in a single dashboard. The tool helps you rapidly and efficiently scale, while reducing risk and accelerating business visibility.
Using the mobile app, staff can create and submit expense reports, enabling supervisors to review and approve expenses during the approval process quickly, easily, and from anywhere on the planet that can connect with a mobile app.
Tipalti’s procurement solutions and AP solutions work to accelerate monthly close by over 25% and reduce your team’s workload with automated reconciliation and tracking. Expense-based transactions and reimbursements are instantly captured and processed just like any other Tipalti-supported payment method.Thanks to it’s robust global payment infrastructure, finance teams can use Tipalti to quickly and easily reimburse employees no matter where they are located. Whether it’s for new office equipment, supplies, or business trips, managers can conveniently review and approve employee expenses via the mobile app.
Expense Report FAQs
How do you create an expense report in Excel?
To create an expense report in Microsoft Excel:
1. Select New in the left menu of the Excel program, or if templates are visible near the top of the opening screen, select view more templates.
2. Search for “expense report” in the “search for online templates” box.
3. Choose and click on the template you like.
4. Click the Create icon.
5. Use and save the template for creating an expense report.
Use a standard expense report template your company has selected and uses companywide.
Who can submit an expense report?
Employees needing reimbursement for business-related expenses can submit an expense report to their company’s payable department. The company’s expense reports are approved for payment by the employee’s authorized supervisor or manager. In some cases, non-employees will also submit an expense to a company for reimbursement.
For example, attorneys will submit an invoice to a client that includes reimbursable expenses incurred in connection with their services. The attorney submits an expense report to their own law firm and charges client-connected expenses to billing codes for later reimbursement.
Airlines are responsible under U.S. Department of Transportation rules for issuing automatic refunds to repay the expenses of customers incurred from delays of at least three hours for domestic flights or six hours for international flights, flight cancellations, and checked bag fees for late delivery of checked luggage. United Airlines canceled 26,700 flights in 2024, at a rate of 1.65% of its total flights. Travel insurance companies may also need to make some payments.
What is a monthly expense report?
A monthly expense report created by an employee is for reimbursement of all of their expenses made on behalf of the company during the period of one month. Employees may also submit expense reports at the end of a business trip instead of accumulating expenses for the entire month.
Businesses may use the term “monthly expense report” to refer to their monthly total business expenses prepared through the bookkeeping process, as summarized in the general ledger or an income statement.
What does the IRS require for expense reports?
The IRS requires documentation for expense reports, including the payee, business purpose, amount, receipts, invoices, and payment records. For tax deductions, businesses must only reimburse employee expense reports for ordinary and necessary business expenses.