What is the Accounting Equation?
The accounting equation is a formula that shows the company’s total assets equal the sum of a company’s liabilities and shareholders’ equity (Assets = Liabilities + Equity).
The clear-cut relationship between a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity is the backbone of the double-entry bookkeeping system. A company’s balance sheet is the source of its accounting equation numbers. Equity can be Shareholders’ Equity, Stockholders’ Equity, or Owner’s Equity.
Like other equations, if two terms of the basic accounting equation are known, you can solve for the third term. For example, Total Assets – Total Liabilities = Total Equity, or Total Assets – Total Equity = Total Liabilities. You move a term from the right side to the left side of the accounting equation by using a minus sign (-).
The accounting equation is also called the balance sheet equation and the fundamental accounting equation. Other names for the balance sheet are statement of financial position or statement of financial condition. The company’s financial position is reflected as a snapshot of account balances from the balance sheet at the end of a reported accounting period.
Key Takeaways
- The accounting equation is a mathematical formula in financial accounting which proves that Total Assets equals Total Liabilities plus Total Equity from a company’s balance sheet.
- The accounting equation is based on the double-entry bookkeeping system, where debits and credits must be equal when recording business transactions and preparing financial statements.
- Accountants view the trial balance to verify that the accounting equation balances before closing the books for an accounting period.
- An unbalanced accounting equation results from unequal recorded debits and credits due to accounting or system posting errors.
What are Specific Names for Equity on the Balance Sheet?
The exact name for Total Equity varies based on a company’s legal entity.
Equity is named Owner’s Equity, Shareholders’ Equity, or Stockholders’ Equity on the balance sheet. Business owners with sole proprietorships and small businesses that aren’t corporations use Owner’s Equity. Corporations with shareholders may call Equity either Shareholders’ Equity or Stockholders’ Equity.
What is Double-Entry Accounting (Bookkeeping)?
In double-entry accounting or bookkeeping, total debits on the left side must equal total credits on the right side. That’s the case for each business transaction and journal entry. As a result of how each recorded accounting transaction affects the general ledger with balanced debits and credits, the financial statements are in balance.
The monthly trial balance lists account names from the chart of accounts with total account balances or amounts. Total debits and credits must be equal before posting transactions to the general ledger for the accounting cycle.
Double-entry bookkeeping started being used by merchants in Italy as a manual system during the 14th century. It is currently used to comply with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP).
Accounting software is a double-entry accounting system that automatically generates the trial balance. The trial balance includes columns with total debit and total credit transactions at the bottom of the report.
Basic Accounting Equation Example – How to Calculate
Here’s a screenshot of Alphabet Inc.’s Consolidated Balance Sheets from its 10-K annual report filing with the SEC for the year ended December 31, 2021. Alphabet Inc. is Google’s parent company. As our example, we compute the accounting equation from the company’s balance sheet as of December 31, 2021. Note that amounts are in millions of dollars.
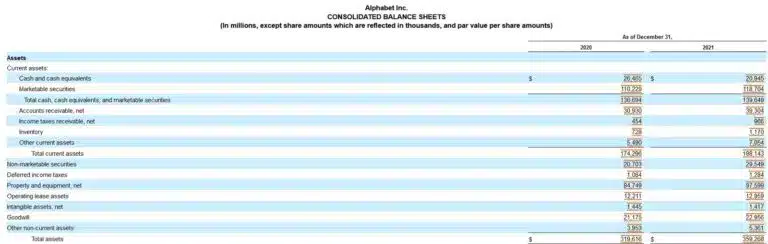
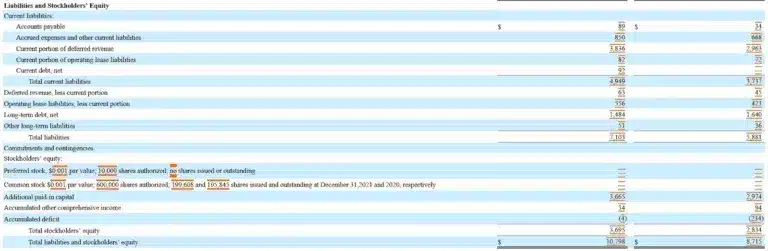
The solution to Alphabet Inc.’s basic Accounting Equation formula is:
Total Assets = Total Liabilities + Total Stockholders’ Equity
$359,268 = $107,633 + $251,635
$359, 268 = $359,268
Because the Alphabet, Inc. calculation shows that the basic accounting equation is in balance, it’s correct. And the double-entry accounting system is working.
What is the Expanded Accounting Equation?
The expanded accounting equation lengthens the basic accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders’ Equity). It shows items within the shareholders’ equity section of the balance sheet in the formula.
The expanded accounting equation (EAE) is:
Total Assets = Total Liabilities + CC +/- AOCIL + BRE + R – E – D – SR
Where terms from the Shareholder’s Equity section of the balance sheet include:
CC is Contributed Capital
AOCIL is Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss)
BRE is Beginning Retained Earnings
R is Revenue
E is Expenses
D is Dividends (paid)
SR is Stock Repurchases
In this expanded accounting equation, CC, the Contributed Capital or paid-in capital, represents Share Capital. AOCIL is added for income or subtracted for loss. Retained Earnings is Beginning Retained Earnings + Revenue – Expenses – Dividends – Stock Repurchases.
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss), AOCIL, is a component of shareholders’ equity besides contributed capital and retained earnings. AOCIL includes unrealized gains or losses on available for sale securities, foreign currency translation gains or losses, and pension plan-related items, including gains or losses, prior pension service costs, and credits.
Share repurchases are called treasury stock if the shares are not retired. Treasury stock transactions and cancellations are recorded in retained earnings and paid-in-capital. The journal entry depends on transaction specifics.
Share capital consists of preferred stock, if any, and common stock. Retained Earnings are computed as Beginning Retained Earnings plus year-to-date additions to Retained Earnings (from Revenue minus Expenses = Net Income) minus Dividends paid minus Share Repurchases.
For EAE, you’ll still need the Balance Sheet. Note that you’ll also need the Income Statement and possibly the detailed Statement of Stockholders’ Equity.
Not all companies will pay dividends, repurchase shares, or have accumulated other comprehensive income or loss.
Can AP automation help keep your accounting equation in balance?
A balanced accounting equation starts with an efficient AP process. Gain control, reduce errors, and improve financial accuracy with expert strategies.
Expanded Accounting Equation Example – How to Calculate
We calculate the expanded accounting equation using 2021 financial statements for this example. To trace the numbers, refer to the same Alphabet Inc. Balance Sheets shown above, as well as the Income Statement and detailed Statement of Stockholder’s Equity in this section.
Alphabet is a tech company that doesn’t pay dividends. The Statement of Stockholders’ Equity shows Alphabet’s share repurchases, which impact both the capital and retained earnings balances.
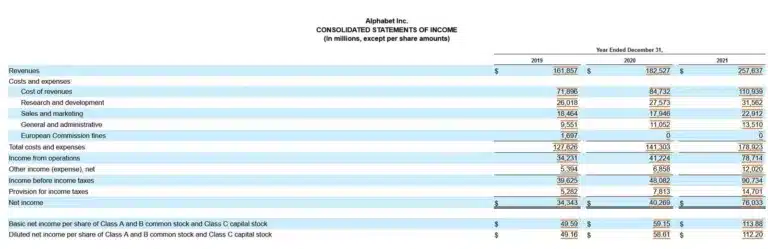
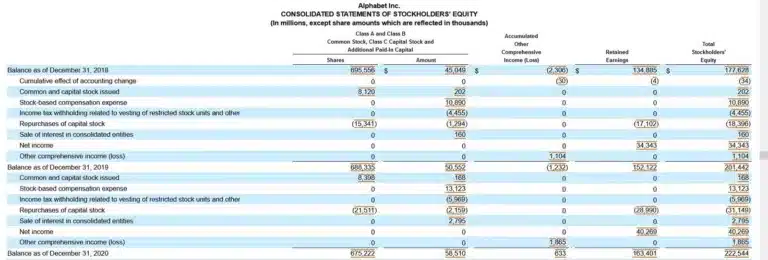
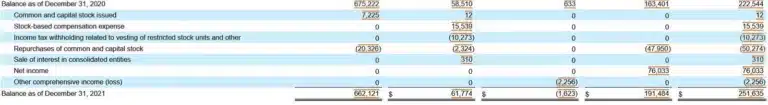
Total Assets = Total Liabilities + CC +/- AOCIL + BRE + R – E – D – SR
$359,268 = $107,633 +((0 + $61,774) – $1,623 + $163,401 + $257,637 – ($178,923 – $12,020 + $14,701) – $0 – $47,950)
$359,268 = $107,633 + ($61,774 – $1,623 + $163,401 + $257,637 – $181,604 – $0 – 47,950)
$359,268 = $107,633 + $251,635
$359,268 = $359,268
How Does the Accounting Equation Differ from the Working Capital Formula?
The accounting equation uses total assets, total liabilities, and total equity in the calculation. This formula differs from working capital, based on current assets and current liabilities.
Working capital measures liquidity. The working capital formula is Current Assets – Current Liabilities.
Current assets include cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, inventory, and prepaid assets. Current liabilities are short-term financial obligations payable in cash within a year. Current liabilities include accounts payable, accrued expenses, and the short-term portion of debt.
Working capital indicates whether a company will have the money needed to pay its bills and other obligations when they are due.
Financial Impacts of an Unbalanced Accounting Equation
If the accounting equation is unbalanced, debits don’t equal credits in the trial balance, and any financial statements generated would be unreliable and inaccurate. Even if the trial balance total debits and credits are equal, as the accounting equation requires, missing transactions may make the financial statements used for financial reporting incomplete and incorrect.
Causes of Unequal Debits and Credits in the Trial Balance
7 causes of unequal debits and credits in the trial balance (an unbalanced accounting equation) are:
- The company’s accounting software has not been adequately tested in implementation and works incorrectly when posting journal entries or other transactions to general ledger accounts.
- A general ledger account is not included in the trial balance.
- The wrong amount is entered in the ledger from an accounting entry source.
- In error, only one side of a journal entry is entered into the system.
- A debit amount is posted as a credit.
- A transposition error occurs (for example, 2305 is entered as 3205).
- A decimal placement error occurs.
Summing It Up
As the fintech industry provides advanced technology applications, memorizing elements of the accounting equation will become obsolete. Well-managed businesses strive to free up human labor to work on value-based vs. routine accounting tasks while automating manual processes. The best accountants and finance professionals need this extra time to contribute to better business results. Learn more about the benefits of accounts payable automation software with integration to your ERP system.
